Introduction
Every year, on July 28th, the world comes together to observe World Hepatitis Day. This global awareness day serves as a reminder of the silent epidemic that it represents and encourages action to prevent, diagnose, and treat this viral disease. It is a group of liver infections that can lead to severe health issues, including liver cirrhosis and cancer. This article explores the significance of World Hepatitis Day, the types of hepatitis, prevention measures, and the global effort to eliminate this public health threat.
It is a liver inflammation that can be caused by a virus, bacteria, or other factors. The most common types of hepatitis are hepatitis A, B, and C.
Hepatitis A
It is caused by the hepatitis A virus (HAV). HAV is spread through the fecal-oral route, which means that it can be transmitted through contaminated food, water, or contact with an infected person’s stool. Symptoms of hepatitis A usually appear within 2 to 6 weeks after exposure and can include:
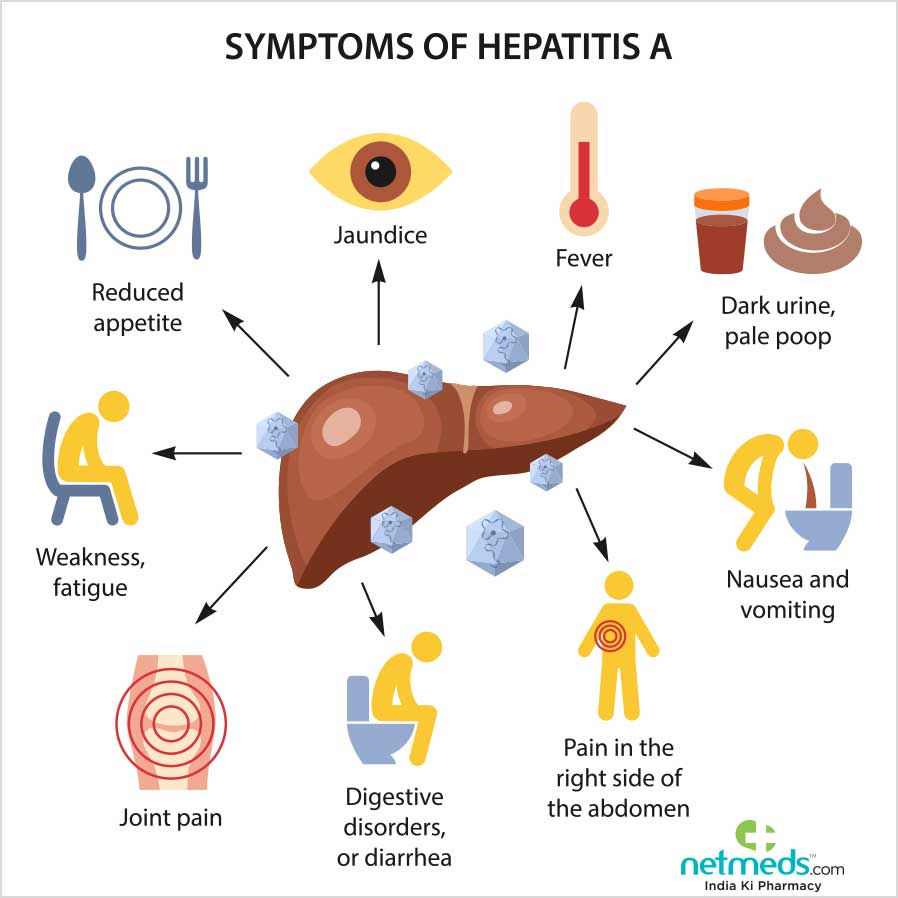
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Dark urine
- Pale stools
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
Weight Loss Tips: What Is The Best Time To Workout?
In most cases, hepatitis A is a mild illness that resolves on its own within a few weeks. However, in some cases, it can lead to more serious complications, such as liver failure.
Hepatitis B
is caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV). HBV is spread through contact with blood, semen, or other bodily fluids. This can happen through sexual contact, sharing needles or other injection drug equipment, or from mother to child during childbirth. Symptoms of hepatitis B can vary from person to person and can range from mild to severe. Some people may not have any symptoms at all. When symptoms do occur, they usually appear within 6 weeks to 6 months after exposure and can include:
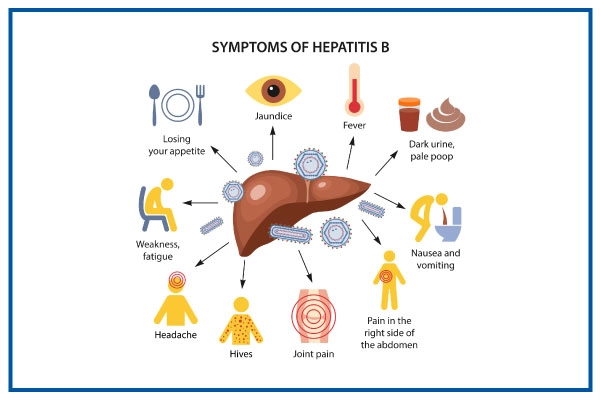
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Dark urine
- Pale stools
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
In some cases, hepatitis B can lead to chronic liver disease, which can eventually lead to liver failure, liver cancer, or death.
Hepatitis C
The virus (HCV) causes it. Infected blood spreads HCV, which can occur through sharing needles or other injection drug equipment, receiving blood or blood products that have not undergone HCV screening, or during childbirth from an infected mother to her child. Symptoms of it can vary from person to person and can range from mild to severe. Some people may not have any symptoms at all. When symptoms do occur, they usually appear within 2 to 6 weeks after exposure and can include:
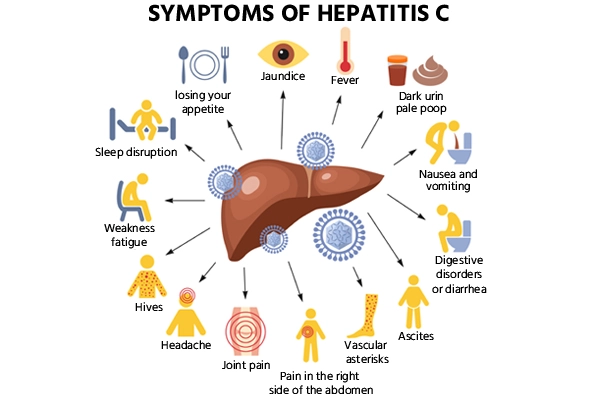
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Dark urine
- Pale stools
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
In some cases, it can lead to chronic liver disease, which can eventually lead to liver failure, liver cancer, or death.
In addition to viral , there are other causes , such as:
- Autoimmune
- Alcoholic
- Drug-induced
- It caused by toxins
If you have any of the symptoms of it, it is important to see a doctor right away. The doctor will perform a physical exam and order blood tests to diagnose the cause of your liver inflammation. Treatment for hepatitis will vary depending on the cause.

