Deep space networking is the process of communicating with spacecraft that are beyond the orbit of Earth. This is a challenging task because the distance between Earth and these spacecraft can be vast, making it difficult to send and receive signals.
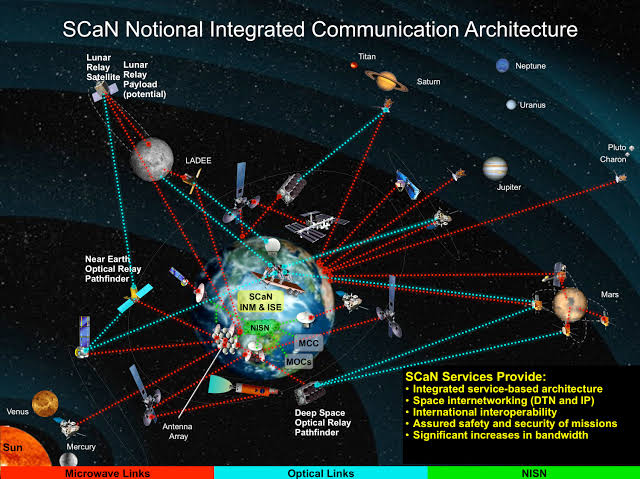
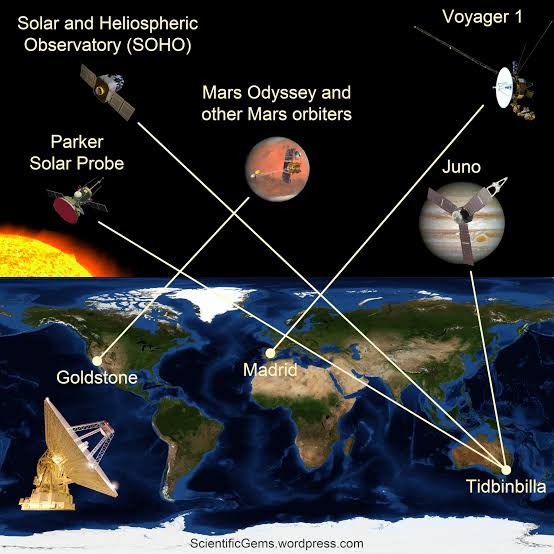
The Deep Space Network (DSN) is a worldwide network of radio antennas that is used to communicate with deep space spacecraft. The DSN consists of three major stations located in California, Spain, and Australia. These stations are spaced approximately 120 degrees apart around the Earth, which allows the DSN to track spacecraft that are moving in any direction.

The DSN uses a variety of radio waves to communicate with spacecraft. The type of radio wave used depends on the distance to the spacecraft and the amount of data that needs to be sent. For example, the DSN uses high-frequency radio waves to communicate with spacecraft that are relatively close to Earth, such as those in orbit around Mars. For spacecraft that are much further away, such as those that are exploring the outer planets, the DSN uses low-frequency radio waves.
The DSN is a vital tool for space exploration. It allows scientists to send commands to spacecraft and to receive data from them. This data can be used to study the planets, moons, and other objects in the solar system. The DSN has also been used to make important discoveries, such as the first images of Pluto and the first images of a black hole.
The DSN is a complex and sophisticated system. It requires a large amount of power and it is constantly being upgraded to meet the demands of new space missions. The DSN is a vital part of NASA’s space exploration program and it will continue to play an important role in the future of space exploration.
Here are some additional details about deep space networking:
- The DSN uses a variety of radio waves to communicate with spacecraft. The type of radio wave used depends on the distance to the spacecraft and the amount of data that needs to be sent.
- The DSN is a vital tool for space exploration. It allows scientists to send commands to spacecraft and to receive data from them. This data can be used to study the planets, moons, and other objects in the solar system.
- The DSN has also been used to make important discoveries, such as the first images of Pluto and the first images of a black hole.
- The DSN is a complex and sophisticated system. It requires a large amount of power and it is constantly being upgraded to meet the demands of new space missions.
- The DSN is a vital part of NASA’s space exploration program and it will continue to play an important role in the future of space exploration.
How DSN works?
Deep space networking works by sending and receiving radio waves between spacecraft and Earth. The Deep Space Network (DSN) is a worldwide network of radio antennas that is used to communicate with deep space spacecraft. The DSN consists of three major stations located in California, Spain, and Australia. These stations are spaced approximately 120 degrees apart around the Earth, which allows the DSN to track spacecraft that are moving in any direction.
The DSN uses a variety of radio waves to communicate with spacecraft. The type of radio wave used depends on the distance to the spacecraft and the amount of data that needs to be sent. For example, the DSN uses high-frequency radio waves to communicate with spacecraft that are relatively close to Earth, such as those in orbit around Mars. For spacecraft that are much further away, such as those that are exploring the outer planets, the DSN uses low-frequency radio waves.
The process of deep space networking can be broken down into the following steps:
- The spacecraft sends a radio signal to the DSN.
- The DSN antenna receives the radio signal.
- The DSN amplifies the radio signal.
- The DSN sends the radio signal to a data processing center.
- The data processing center decodes the radio signal.
- The data processing center sends the data to scientists.
The time it takes for a radio signal to travel from Earth to a spacecraft and back again depends on the distance between Earth and the spacecraft. For example, it takes about 4 minutes for a radio signal to travel from Earth to Mars. This means that there is a 4-minute delay between the time a command is sent to a spacecraft and the time the spacecraft receives the command.
The DSN is a vital tool for space exploration. It allows scientists to send commands to spacecraft and to receive data from them. This data can be used to study the planets, moons, and other objects in the solar system. The DSN has also been used to make important discoveries, such as the first images of Pluto and the first images of a black hole.
The DSN is a complex and sophisticated system. It requires a large amount of power and it is constantly being upgraded to meet the demands of new space missions. The DSN is a vital part of NASA’s space exploration program and it will continue to play an important role in the future of space exploration.

