The birth and expansion of the universe is a complex topic that is still being studied by scientists. However, we do know a few things about how the universe began and how it has evolved over time.
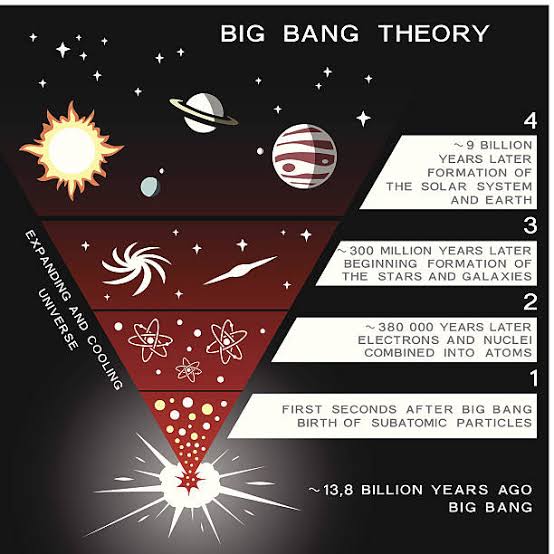
The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological model for the universe. It states that the universe was once in an extremely hot and dense state that expanded rapidly. This expansion caused the universe to cool and resulted in its present size and composition.
The Big Bang theory is supported by a wide range of evidence, including the cosmic microwave background radiation, the abundance of light elements in the universe, and the redshift of distant galaxies.
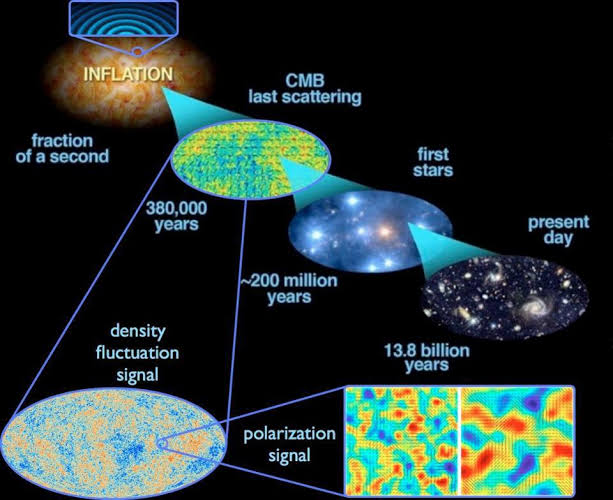
The cosmic microwave background radiation is a faint afterglow of the initial explosion. It was discovered in 1965 by Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson, and it provides strong evidence that the universe began with a hot, dense state.

The abundance of light elements in the universe is also consistent with the Big Bang theory. These elements, such as hydrogen, helium, and lithium, were created in the initial explosion. The Big Bang theory predicts the correct abundance of these elements, which is further evidence that the theory is correct.
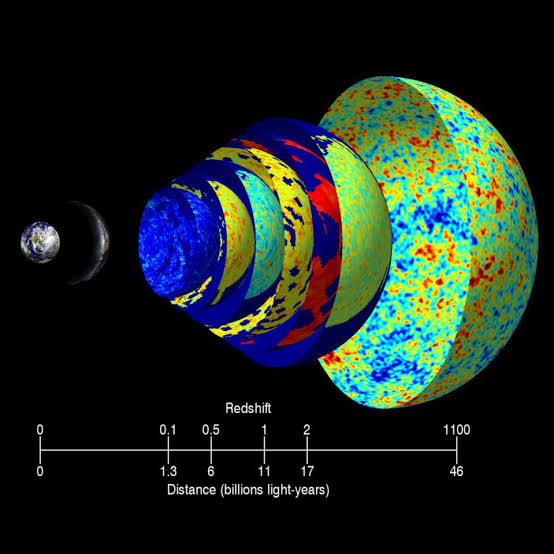
The redshift of distant galaxies is another piece of evidence that supports the Big Bang theory. Redshift is a phenomenon in which the light from distant galaxies is stretched, making it appear redder. This stretching is caused by the expansion of the universe. The amount of redshift is proportional to the distance to the galaxy, which is consistent with the Big Bang theory.
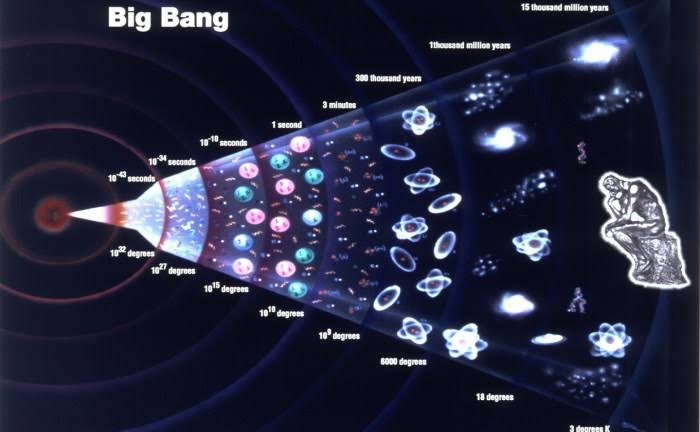
The Big Bang theory is not without its challenges. One challenge is that it does not explain what caused the initial explosion. Another challenge is that it does not explain why the universe is expanding at an accelerating rate.
Despite these challenges, the Big Bang theory is the best explanation we have for the origin and evolution of the universe. It is a well-tested theory that is supported by a wide range of evidence.
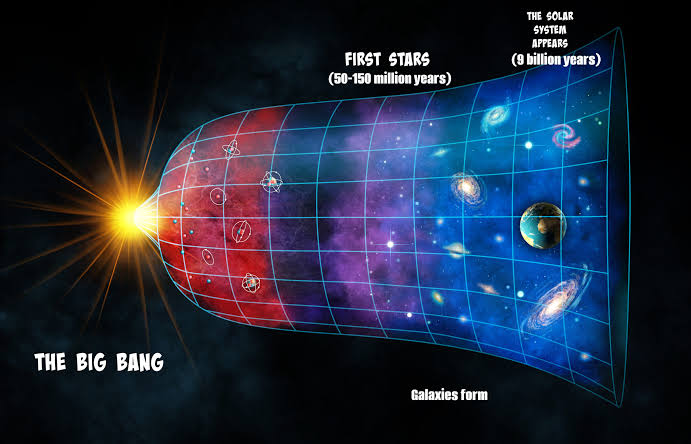
The expansion of the universe is a direct consequence of the Big Bang theory. As the universe expanded, it cooled and allowed for the formation of matter and energy. The expansion of the universe is still ongoing, and it is accelerating due to the presence of dark energy.

Dark energy is a mysterious substance that makes up about 70% of the universe. It is thought to be responsible for the accelerating expansion of the universe. The nature of dark energy is not fully understood, but it is one of the most important unsolved problems in cosmology.
The expansion of the universe has a number of implications for the future of the universe. If the expansion continues to accelerate, the universe will eventually become too large and cold for life to exist. However, if the expansion eventually slows or stops, the universe may eventually collapse in on itself in a “Big Crunch.”
The ultimate fate of the universe is unknown, but the expansion of the universe is one of the most important factors that will determine its future.
Here is a more detailed timeline of the birth and expansion of the universe:
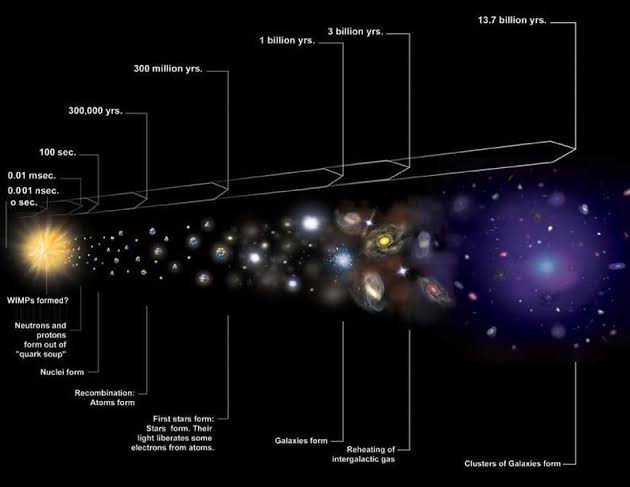
- 10^−36 seconds: The universe is born in a massive explosion called the Big Bang.
- 10^−32 seconds: The universe is filled with a hot, dense soup of elementary particles.
- 10^−6 seconds: The universe cools enough for quarks to combine into protons and neutrons.
- 1 second: The universe cools enough for electrons to combine with protons and neutrons to form atoms of hydrogen and helium.
- 380,000 years: The universe is no longer opaque to light, and the cosmic microwave background radiation is released.
- 13.8 billion years: The universe is as it is today, with galaxies, stars, and planets.
The universe is a vast and mysterious place, and we are only just beginning to understand its origins and evolution. The Big Bang theory is a powerful tool that has helped us to understand the universe, but there are still many unanswered questions. As we continue to study the universe, we may one day uncover the secrets of its birth and expansion.