Introduction
In the vast expanse of space, Earth’s orbit is becoming increasingly cluttered with defunct satellites, spent rocket stages, and fragments from previous space missions. This accumulation of debris poses a growing threat to active satellites, space stations, and future space exploration endeavors. Enter Astro Scale, a pioneering company on a mission to clean up the mess in Earth’s orbit. In this article, we’ll explore the innovative technology behind Astro Scale’s new robot tug, its mission to tackle orbital debris, and the implications of this groundbreaking initiative.
The Growing Problem of Space Debris -Astro Scale’s Robot Tug
A Crowded Cosmos
As humanity’s presence in space has expanded, so too has the amount of space debris. Thousands of defunct satellites, rocket parts, and other remnants now orbit the Earth, creating a hazardous environment for active spacecraft.
The Kessler Syndrome
The increasing density of space debris has raised concerns about the Kessler Syndrome, a theoretical scenario where collisions between debris generate more fragments, leading to a cascade of collisions and a rapidly deteriorating orbital environment.
Astro Scale: A Space Cleanup Pioneer -Astro Scale’s Robot Tug
Innovative Technology
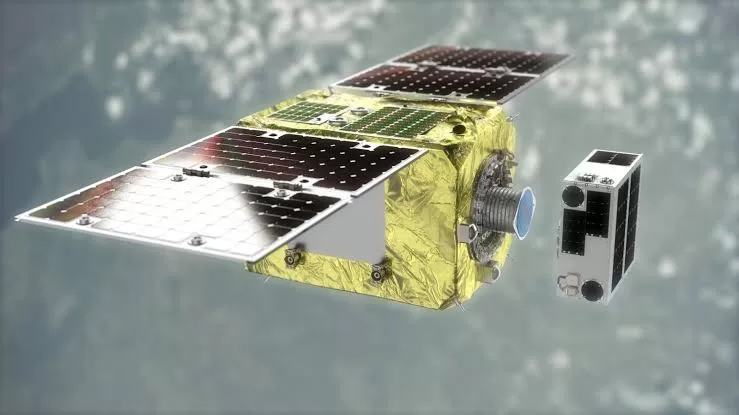
Astro Scale has developed a cutting-edge solution to the space debris problem. Their robot tug, equipped with advanced sensors and propulsion systems, can rendezvous with defunct satellites and safely remove them from orbit.
The Vision
Astro Scale envisions a future where space is free from the looming threat of debris collisions. Their technology aims to preserve the long-term sustainability of space activities.
How the Robot Tug Works – Astro Scale’s Robot Tug
Autonomous Rendezvous
The robot tug employs autonomous navigation to approach and dock with defunct satellites. This process minimizes the risk of collisions during cleanup operations.
Controlled Deorbiting – Astro Scale’s Robot Tug
Once attached to a piece of debris, the robot tug uses its propulsion system to lower the satellite’s orbit. Eventually, the satellite re-enters Earth’s atmosphere and burns up, eliminating the threat it posed.
Multiple Missions – Astro Scale’s Robot Tug
It is designed for multiple missions, ensuring that it can tackle numerous targets and contribute significantly to space debris removal.
Implications for Space Exploration – Astro Scale’s Robot Tug
Safer Space Activities
The removal of space debris by it enhances the safety of space missions, reducing the risk of spacecraft collisions.
Sustainability – Astro Scale’s Robot Tug
A cleaner orbital environment promotes the sustainability of space activities, making it easier for future generations to explore and utilize space.
Conclusion
It is a remarkable advancement in the quest to clean up Earth’s orbit. By addressing the issue of space debris head-on, this innovative technology not only safeguards existing space assets but also paves the way for a more sustainable and secure future in space exploration.
FAQs
- What is space debris, and why is it a problem? Space debris refers to defunct satellites, rocket parts, and other fragments in Earth’s orbit. It poses a problem because it increases the risk of collisions with active spacecraft.
- How does it remove space debris? It uses advanced sensors and propulsion systems to rendezvous with and deorbit defunct satellites, ensuring their safe removal from orbit.
- What is the Kessler Syndrome, and why is it concerning? The Kessler Syndrome is a scenario where collisions between space debris generate more fragments, leading to a cascade of collisions and a deteriorating orbital environment, making space activities riskier.
- Why is space debris removal important for space exploration? Space debris removal enhances the safety and sustainability of space activities, reducing the risk of spacecraft collisions and preserving space for future generations.

