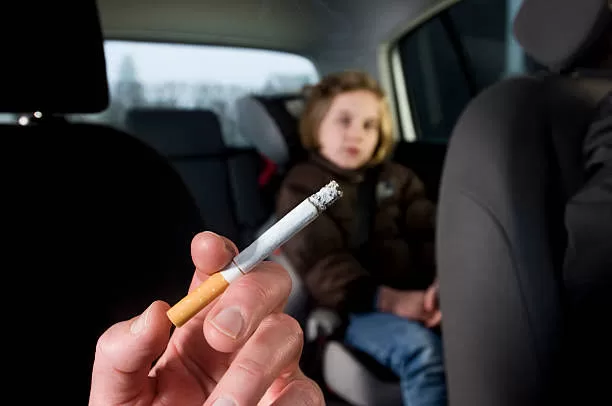
Passive smoking, also known as secondhand smoke, is breathing in the smoke from someone else’s cigarette, cigar, or pipe. It can be just as harmful as smoking, and there is no safe level of exposure.
The health risks of passive smoking include:
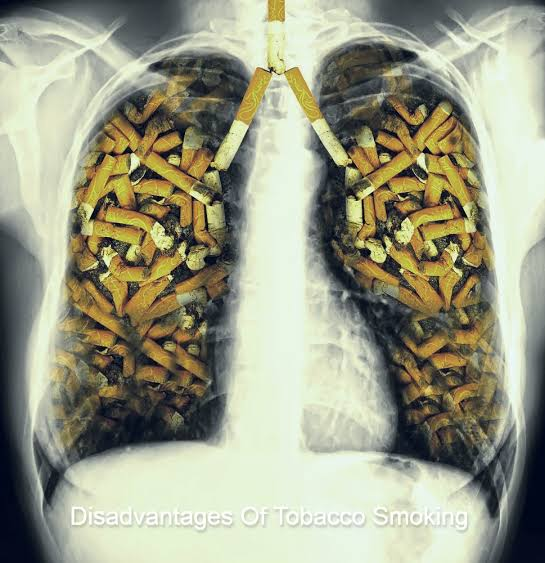
- Lung cancer: Passive smoking increases the risk of lung cancer by 20-30% in adults who do not smoke.
Heart disease – Passive smoking:
increases the risk of heart disease by 25-30% in adults who do not smoke.
Stroke: It increases the risk of stroke by 20-30% in adults who do not smoke.
Low birth weight: Passive smoking during pregnancy increases the risk of low birth weight in babies.
Asthma: Passive smoking can trigger asthma attacks and make asthma worse.
Sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS): It increases the risk of SIDS in babies.
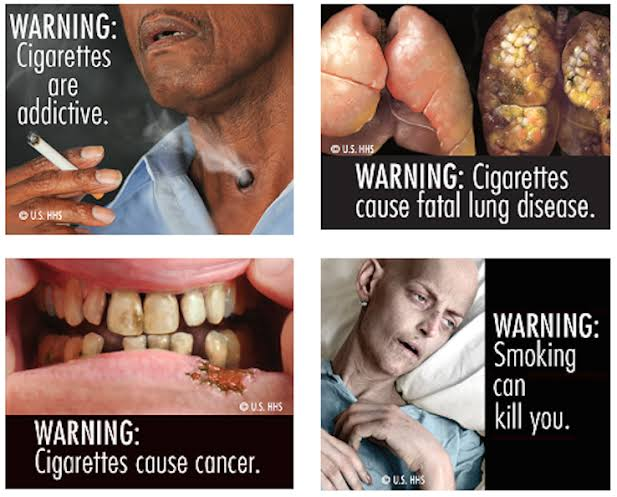
In addition to these specific health risks, It can also cause a number of other health problems, including:
- Respiratory infections: It can increase the risk of respiratory infections such as bronchitis, pneumonia, and ear infections.
- Eye problems: It can increase the risk of eye problems such as cataracts and age-related macular degeneration.
- Reduced lung function: It can reduce lung function and make it harder to breathe.
- Cancers of the mouth, throat, and larynx: It increases the risk of cancers of the mouth, throat, and larynx.
There is no safe level of exposure to it. If you are exposed, it is important to try to reduce your exposure as much as possible. You can do this by:
- Avoiding places where people smoke. This includes your home, your workplace, and public places.
- Asking people not to smoke around you. If someone does smoke around you, ask them to move away or to smoke outside.
- Opening windows and doors to ventilate the area. This will help to reduce the amount of secondhand smoke in the air.
If you are concerned about the health risks of passive smoking, talk to your doctor. They can help you to reduce your exposure and to protect your health.

