The Indian government’s decision to slash subsidies for electric two-wheelers (E2Ws) has had a devastating impact on the industry, with sales plummeting and manufacturers struggling to stay afloat.
The subsidy mess began in June 2023, when the government announced that it would be reducing the subsidy for E2Ws from 40% to 15%. This decision came as a shock to the industry, as it had been expecting the subsidy to remain at 40% for the remainder of the FAME-II scheme, which is due to end in March 2024.
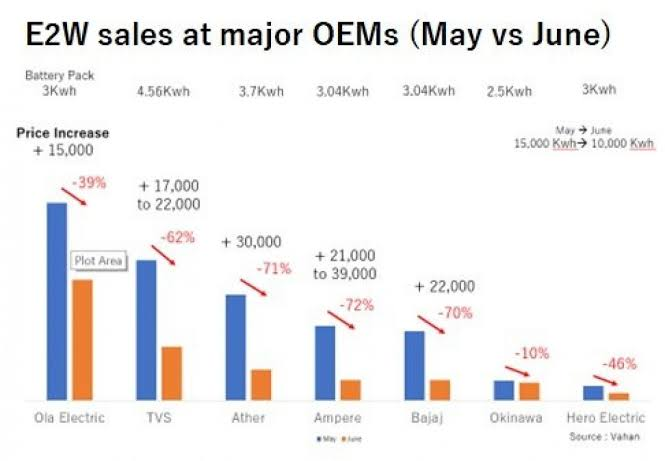
The reduction in the subsidy has led to a sharp decline in E2W sales. In June 2023, sales of E2Ws fell by 57% compared to the previous month. This is the lowest level of sales in the last 12 months.
The subsidy reduction has also put a strain on E2W manufacturers’ finances. Many manufacturers had already invested heavily in production capacity in anticipation of continued high demand for E2Ws. However, with the sudden decline in sales, many manufacturers are now struggling to repay their loans and keep their businesses afloat.
The subsidy mess has also led to job losses in the E2W industry. Hero Electric, one of the largest E2W manufacturers in India, has announced that it will be laying off 1,000 employees. Other manufacturers are also expected to announce job cuts in the coming weeks.
The subsidy mess is a major setback for the Indian E2W industry. The industry was already facing challenges, such as the high cost of batteries and the lack of charging infrastructure. The subsidy reduction has made it even more difficult for E2W manufacturers to compete with petrol-powered two-wheelers.
The government needs to take urgent steps to address the subsidy mess and revive the E2W industry. The government could consider increasing the subsidy for E2Ws, or providing other financial incentives to manufacturers. The government could also invest in developing charging infrastructure, which would make E2Ws more attractive to consumers.
Without urgent action from the government, the Indian E2W industry could collapse. This would be a major setback for India’s efforts to promote green transportation and reduce its reliance on fossil fuels.

